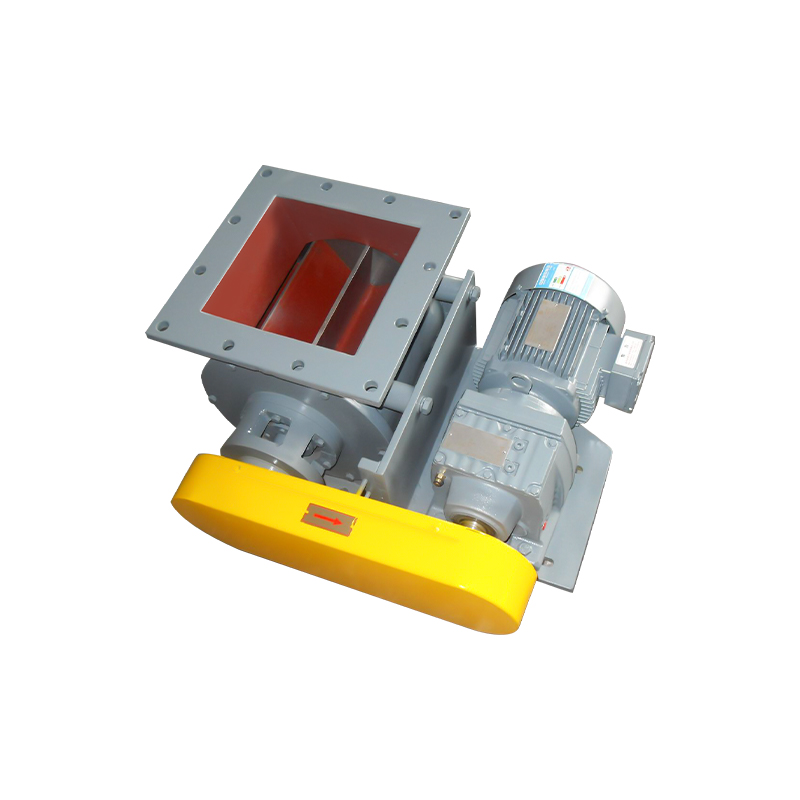
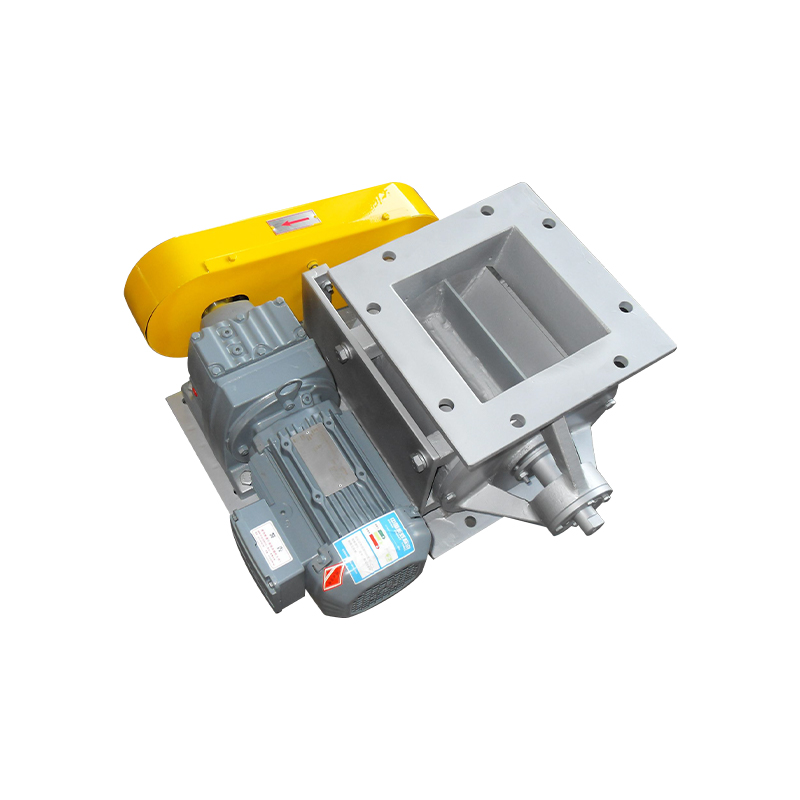
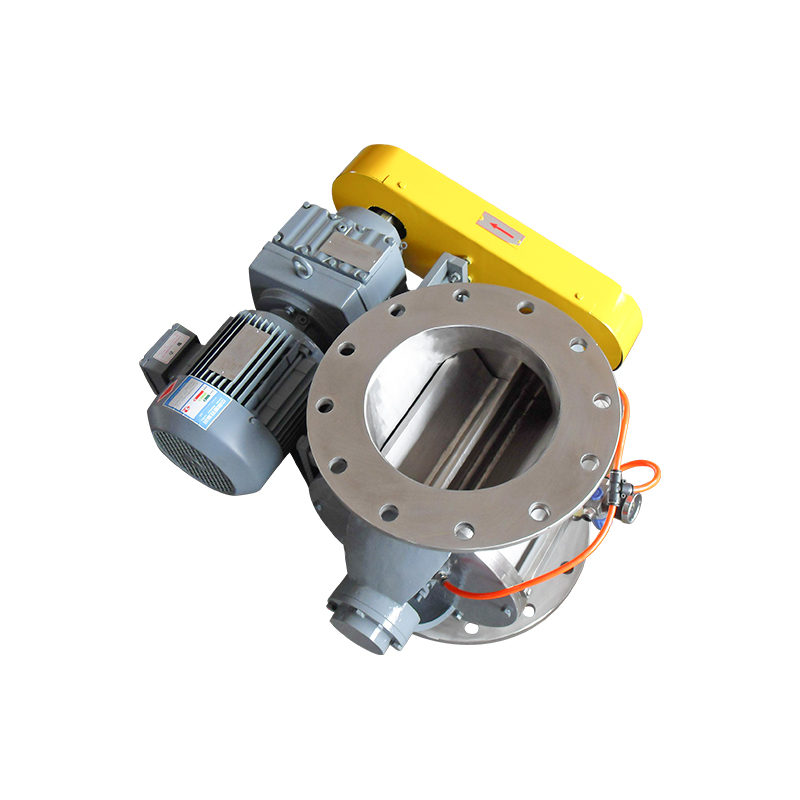
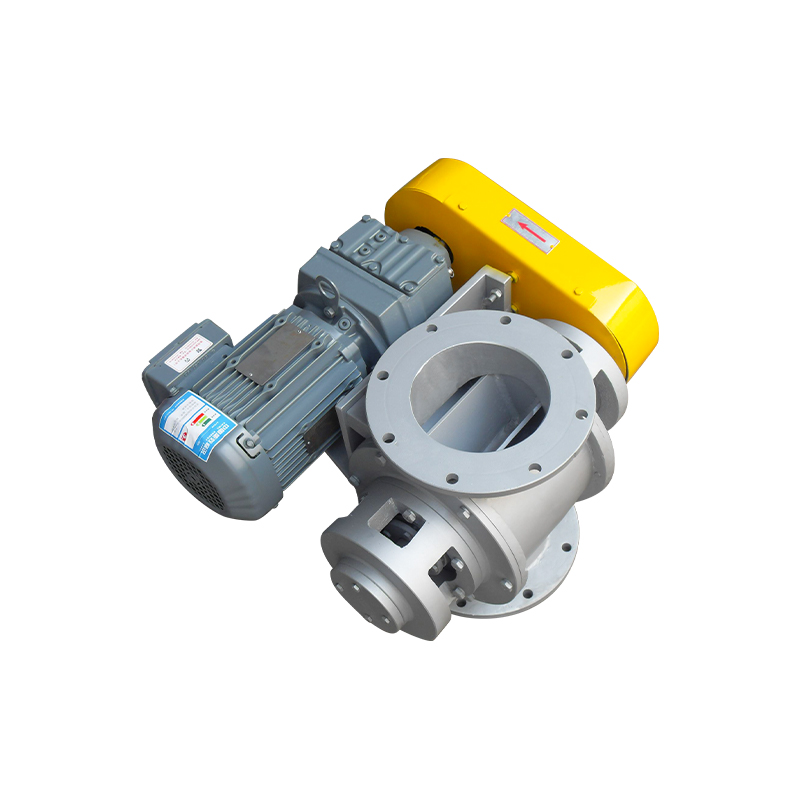
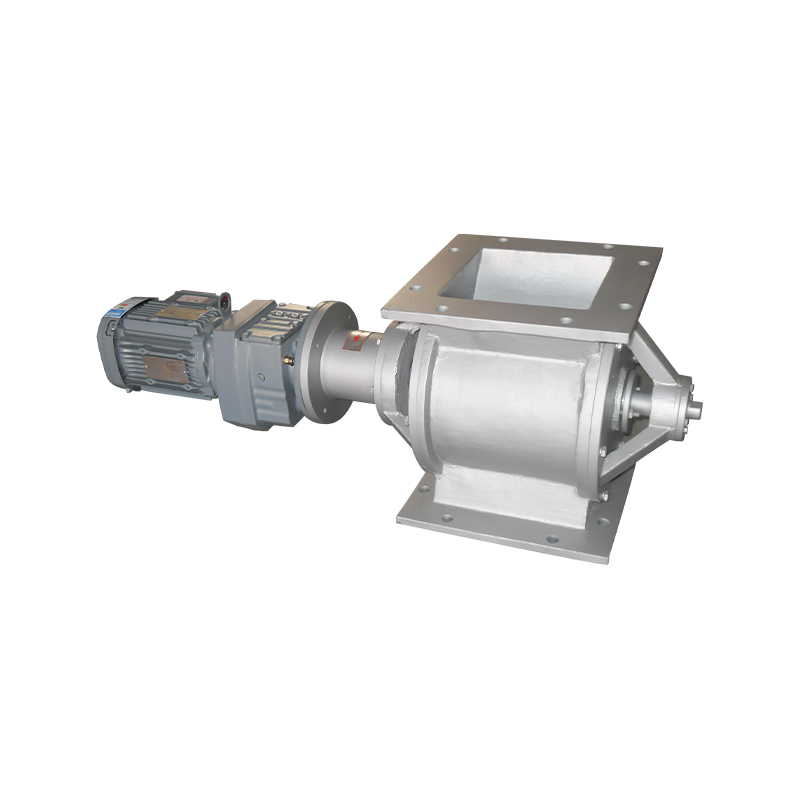
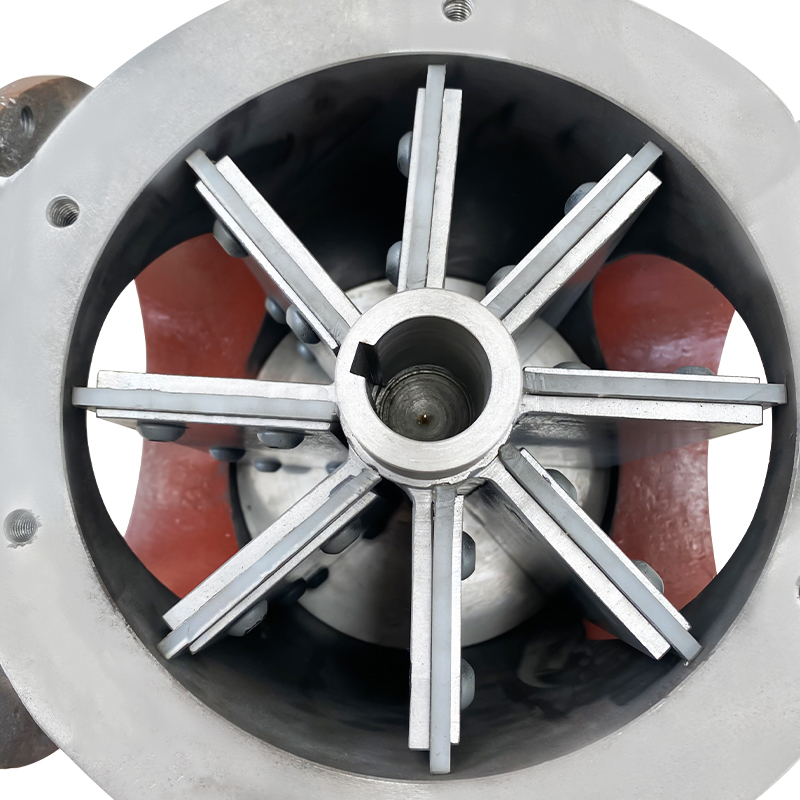
Square port rotary discharge valves, also known as rotary airlock valves or rotary feeders with square outlet configurations, represent a specialized category of material handling equipment designed to control the flow of bulk solids while maintaining air seal integrity between different pressure zones. Unlike traditional round port designs, square port configurations feature rectangular or square-shaped discharge openings that align with the rotor pockets, maximizing material discharge efficiency and minimizing product degradation. This geometric advantage allows for more complete pocket evacuation and reduced material holdup, particularly beneficial when handling sticky, cohesive, or fragile materials.
The fundamental operating principle involves a multi-vane rotor housed within a precision-machined body, rotating continuously to accept material from an inlet hopper or conveying system and discharge it through the square port outlet. Each rotor pocket acts as an isolated chamber that moves material from the inlet to the discharge position while preventing air leakage between zones of different pressures. The square port geometry ensures that as the rotor pocket reaches the discharge position, the entire pocket opening aligns precisely with the square outlet port, creating an unobstructed path for material to exit under the influence of gravity and centrifugal force.
Construction materials and clearance tolerances critically influence performance characteristics and application suitability. Premium units feature cast iron or fabricated steel housings with hardened steel or stainless steel rotors, while specialized applications may require exotic alloys, abrasion-resistant coatings, or food-grade stainless steel construction. Rotor-to-housing clearances typically range from 0.003 to 0.010 inches per side, balancing air seal effectiveness against wear accommodation and thermal expansion requirements. Tighter clearances provide superior air sealing but reduce tolerance for abrasive materials and thermal cycling, while looser clearances sacrifice some sealing capability for enhanced durability in demanding applications.
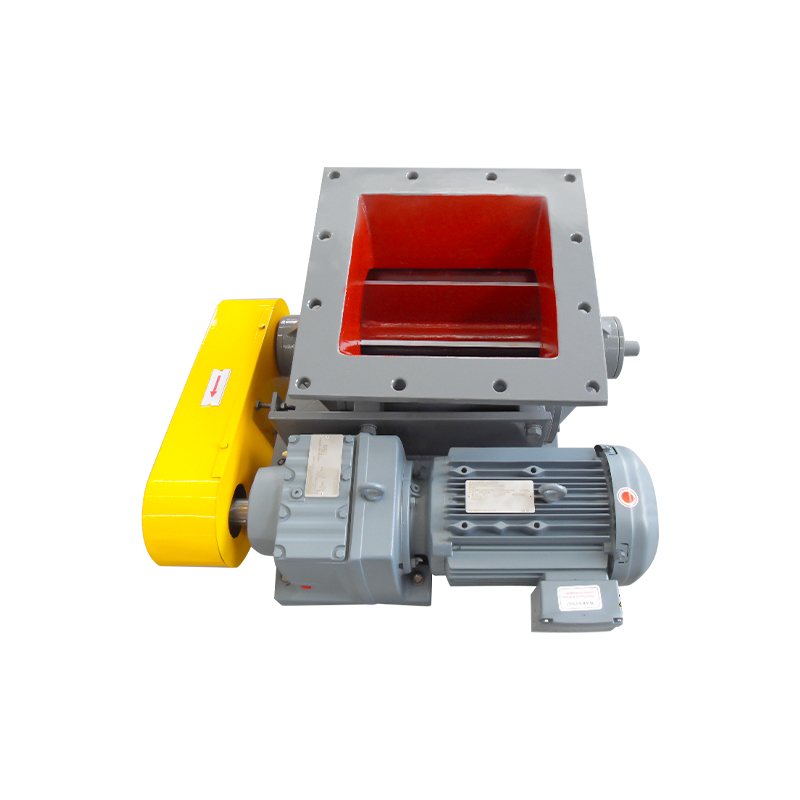

Advantages of Square Port Configuration Over Round Port Designs
The square port discharge opening delivers measurable performance advantages in specific material handling scenarios, particularly when managing difficult-to-handle products. The primary benefit stems from improved pocket evacuation efficiency, as the square geometry closely matches the rectangular shape of the rotor pockets, creating minimal restriction as material exits the valve. This design characteristic reduces the tendency for material to bridge across the discharge opening or accumulate in pocket corners, problems commonly encountered with round port configurations where circular openings create flow restrictions at pocket edges.
Product degradation reduction represents another significant advantage, especially critical when handling fragile materials such as plastic pellets, food products, or crystalline chemicals. Round port valves create a pinch point where material must compress and squeeze through the circular opening, generating shear forces that can break particles, generate fines, or damage product structure. Square ports eliminate this compression zone, allowing material to flow freely from the rotor pocket without dimensional restriction, preserving product integrity throughout the discharge process.
- Enhanced flow characteristics for sticky or cohesive materials that tend to adhere to valve surfaces and resist complete discharge through restricted openings
- Reduced power consumption due to decreased resistance during material discharge, particularly noticeable in high-capacity applications processing hundreds or thousands of pounds per hour
- Improved accuracy in metering applications where complete pocket evacuation ensures consistent volumetric delivery with minimal carryover or residual material
- Simplified cleaning and maintenance access through larger, more accessible discharge openings that facilitate inspection and removal of any material buildup or foreign objects
Primary Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Pneumatic conveying systems extensively deploy square port rotary discharge valves at critical transfer points where material must transition between atmospheric pressure and positive or negative pressure conveying lines. In dilute phase pneumatic systems, these valves feed material into high-velocity air streams while preventing backflow of conveying air into upstream storage vessels or process equipment. The superior sealing characteristics and complete pocket evacuation of square port designs ensure consistent feed rates and reliable system performance, particularly important in applications where irregular material feeding causes conveying line plugging or product quality variations.
Food processing facilities utilize square port rotary valves for handling delicate products requiring gentle treatment and minimal breakage. Applications include feeding flour, sugar, cocoa powder, coffee beans, breakfast cereals, snack foods, and pet food ingredients into packaging lines, blending systems, or cooking processes. The sanitary design variants with polished stainless steel construction, FDA-approved materials, and easy disassembly for cleaning comply with stringent food safety regulations while the square port geometry preserves product appearance and texture throughout handling operations.
Chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing operations depend on square port rotary discharge valves for accurate metering and contamination-free handling of active ingredients, excipients, and finished products. These applications demand precise flow control, complete material containment, and compatibility with corrosive or reactive substances. Square port configurations excel in these roles by providing consistent volumetric delivery, minimizing cross-contamination through complete pocket evacuation, and accommodating specialized materials of construction including Hastelloy, titanium, or PTFE-lined components for extreme chemical resistance.
Material Characteristics and Compatibility Considerations
Successful valve selection requires careful evaluation of material properties and their interaction with valve design features. Particle size distribution significantly influences rotor pocket sizing and clearance requirements, with fine powders requiring tighter clearances to prevent leakage while coarse granules tolerate larger clearances without excessive air bypass. Square port valves accommodate wider particle size ranges than round port designs because the unrestricted discharge opening prevents bridging of large particles while still effectively handling fines without degradation.
Bulk density and flowability characteristics determine appropriate rotor speed and pocket volume selections. Free-flowing materials with bulk densities below 50 pounds per cubic foot operate effectively at higher rotational speeds (30-40 RPM) with smaller pocket volumes, while dense or sluggish materials (bulk density above 70 pounds per cubic foot) benefit from slower speeds (10-20 RPM) and larger pockets to ensure complete filling and discharge. The square port geometry particularly benefits difficult-flowing materials by eliminating discharge restrictions that could impede gravity flow from rotor pockets.
| Material Property | Consideration for Square Port Valves | Design Adaptation |
| Abrasive Materials | Accelerated wear on rotor tips and housing | Hardened surfaces, replaceable wear parts |
| Sticky/Cohesive | Material buildup in pockets and ports | Polished surfaces, purge air options |
| Fragile Products | Particle breakage during discharge | Reduced tip speeds, open pocket design |
| High Temperature | Thermal expansion affects clearances | Special alloys, water cooling jackets |
| Hygroscopic | Moisture absorption causes caking | Sealed construction, purge gas injection |
| Explosive Dust | Ignition risk from friction/static | Explosion-proof motors, grounding |
Sizing and Capacity Determination Methods
Proper valve sizing balances throughput requirements against material handling characteristics and system constraints. Capacity calculations begin with determining the required volumetric or mass flow rate, then working backward to establish appropriate rotor dimensions and operating speed. The fundamental sizing equation relates pocket volume, number of pockets, rotational speed, and fill efficiency to achieve target capacity. Square port valves typically achieve fill efficiencies between 60% and 85% depending on material flowability, with free-flowing materials approaching the upper range while cohesive materials fall toward the lower end.
Rotor diameter selection influences both capacity and air leakage characteristics, with larger diameter rotors providing greater pocket volumes and higher capacity potential but also creating longer sealing perimeters that may increase air bypass. Common rotor diameters range from 6 inches for small metering applications to 24 inches or larger for high-volume bulk handling, with 8-inch, 10-inch, and 12-inch sizes representing popular general-purpose options. The square port outlet dimensions typically match or slightly exceed the rotor diameter to ensure unrestricted discharge, though some designs optimize port sizing based on downstream equipment requirements.
Speed and Pocket Configuration Optimization
Rotational speed selection involves trade-offs between capacity, product degradation, air leakage, and wear rate. Higher speeds increase throughput capacity but also elevate centrifugal forces that can damage fragile materials, accelerate component wear, and compromise air seal effectiveness through reduced dwell time in sealing zones. Most square port rotary discharge valves operate between 15 and 35 RPM, with variable frequency drives enabling speed adjustment to fine-tune capacity or accommodate different materials without mechanical modifications.
Pocket configuration encompasses both the number of vanes (typically 6, 8, or 10) and the depth or volume of each pocket. More pockets reduce the individual pocket volume required for a given capacity, potentially allowing smaller overall valve size, but increase manufacturing complexity and create more sealing interfaces where air leakage can occur. Deeper pockets accommodate larger particle sizes and improve capacity for a given rotor diameter but may compromise complete evacuation of sticky materials. Square port designs partially mitigate this concern through unrestricted discharge geometry that aids pocket clearing.
Installation Best Practices and System Integration
Proper installation begins with adequate structural support capable of handling static equipment weight plus dynamic loads from material flow, vibration, and thermal expansion. Square port rotary valves should be mounted on rigid foundations or structural steel frameworks that prevent misalignment from settling or deflection. Mounting orientation typically positions the valve vertically with material entering from above, though horizontal or inclined installations are possible in specific applications with appropriate design modifications to ensure complete pocket filling and discharge.
Inlet connection design significantly influences feeding consistency and valve performance. The inlet hopper or chute should provide a minimum of 6-12 inches of material head pressure above the valve inlet to ensure consistent pocket filling, with hopper outlet dimensions matching or slightly exceeding the valve inlet opening. Mass flow hopper designs prevent bridging and ratholing while maintaining steady material supply, particularly important for cohesive or irregular-shaped materials. Inlet transition geometry should avoid sharp angles or flow restrictions that create turbulence or uneven material distribution across the valve inlet.
Discharge connections must accommodate the square port geometry while providing smooth material transition to downstream equipment. Flexible connections or expansion joints between the valve outlet and rigid downstream piping prevent stress transmission from thermal expansion, vibration, or equipment settlement. For pneumatic conveying applications, the discharge configuration should minimize air turbulence and maintain consistent material acceleration into the conveying line, often achieved through carefully designed venturi sections or injector nozzles positioned immediately downstream of the square port outlet.
Maintenance Requirements and Service Life Optimization
Routine maintenance programs for square port rotary discharge valves focus on preserving critical clearances, preventing material buildup, and monitoring wear progression. Weekly or monthly inspection intervals should include visual examination of accessible components, listening for unusual noises indicating bearing problems or rotor contact, and monitoring drive motor current draw for changes suggesting increased friction or material loading. Bearing lubrication follows manufacturer schedules, typically requiring greasing every 500-2000 operating hours depending on bearing type, load conditions, and environmental factors.
Rotor-to-housing clearance monitoring represents the most critical predictive maintenance task, as excessive clearance allows air leakage that compromises system performance while insufficient clearance causes rotor-to-housing contact and catastrophic failure. Clearance measurements require periodic valve disassembly using feeler gauges or specialized measurement tools, with replacement of worn components recommended when clearances exceed 200-300% of original specifications. The square port configuration facilitates this inspection process through the large discharge opening that provides excellent visual access to rotor condition and wear patterns.
- Scheduled replacement of rotor tips or vanes at predetermined intervals based on material abrasiveness and operating hours extends overall valve service life while preventing unexpected failures
- Regular cleaning removes material accumulations that interfere with proper operation, particularly important for sticky or hygroscopic materials that build up during idle periods
- Shaft seal inspection and replacement prevents material leakage along the drive shaft and contamination of bearing housings, with seal selection based on material properties and environmental conditions
- Drive system maintenance including belt tension adjustment, coupling alignment, and motor bearing service ensures reliable power transmission and prevents vibration-related problems
Troubleshooting Common Operational Issues
Inconsistent or reduced material flow often indicates pocket filling problems, discharge restrictions, or wear-related clearance issues. Systematic troubleshooting begins by verifying adequate material supply to the valve inlet, checking for bridging or ratholing in upstream hoppers, and confirming proper inlet hopper design for the material being handled. If supply issues are eliminated, internal inspection may reveal material buildup on rotor surfaces, worn pockets reducing effective volume, or damaged vanes preventing complete pocket formation.
Excessive air leakage through the valve manifests as difficulty maintaining system pressure, increased pneumatic conveying line velocities, or compromised process conditions in sealed vessels. Root causes include excessive rotor-to-housing clearances from wear, damaged or deformed rotor components, thermal expansion creating temporary clearance increases, or improper assembly leaving gaps at mating surfaces. The square port design minimizes some leakage pathways compared to round port configurations, but systematic clearance verification and component replacement remain necessary when leakage exceeds acceptable limits.
Product degradation or quality problems traced to the rotary valve may result from excessive tip speeds generating shear forces, rotor contact with housing creating contamination from metal wear particles, or material residence time in pockets allowing degradation from heat or chemical reactions. Solutions include reducing rotational speed to lower centrifugal forces and shear rates, restoring proper clearances to prevent contact, or implementing cooling systems for temperature-sensitive materials. The square port geometry's inherent advantage in minimizing discharge restriction helps preserve product quality, but proper operating parameters remain essential.
Advanced Features and Technology Enhancements
Modern square port rotary discharge valves incorporate sophisticated features that enhance performance, reliability, and integration with automated systems. Variable frequency drives enable precise speed control for accurate flow rate adjustment without mechanical changes, supporting multi-product facilities or processes with varying throughput requirements. Remote monitoring capabilities through integrated sensors track operating parameters including rotational speed, drive motor current, bearing temperature, and vibration levels, transmitting data to central control systems for real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Purge air injection systems address challenges with sticky or cohesive materials by introducing low-pressure air into rotor pockets just before the discharge position, assisting material evacuation and preventing buildup. These systems require careful pressure regulation to avoid back-pressurizing upstream equipment or disturbing material flow patterns. Heating or cooling jacket options maintain optimal temperature conditions for materials sensitive to thermal variations, with jacketed models accommodating heating fluids, cooling water, or direct steam injection depending on process requirements.
Explosion-proof and dust-ignition-proof designs meet stringent safety requirements for handling combustible dusts in industries including grain processing, chemical manufacturing, and plastics production. These specialized valves incorporate non-sparking materials, grounded components to prevent static accumulation, explosion-proof motor enclosures, and pressure relief provisions that safely vent internal explosions without propagating to connected equipment. Certification to ATEX, IECEx, or NFPA standards ensures compliance with regional safety regulations while the square port geometry's reduced shear characteristics may lower ignition risk compared to more restrictive discharge configurations.


 English
English عربى
عربى