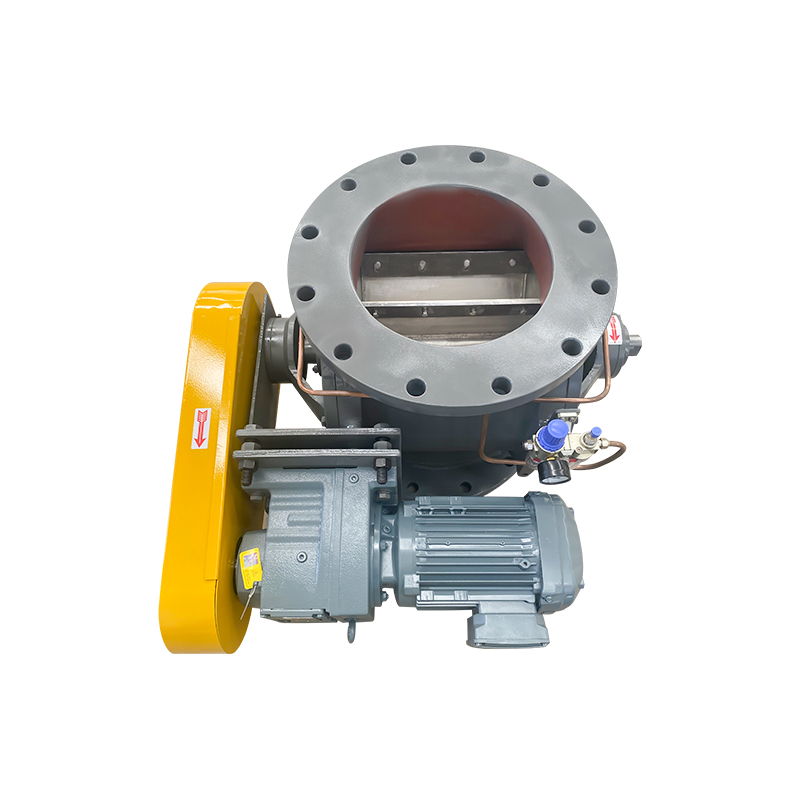
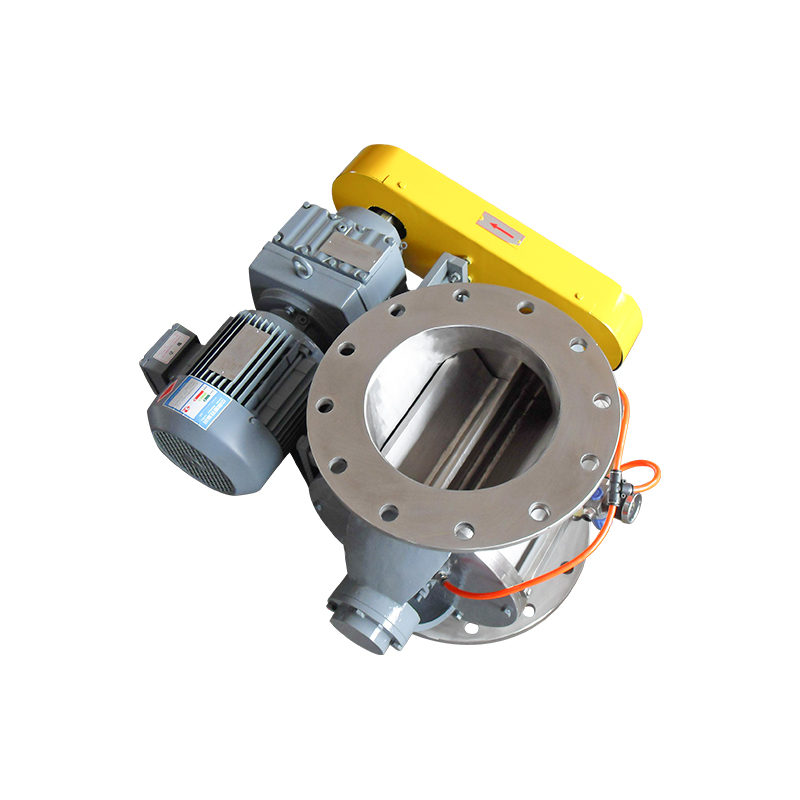
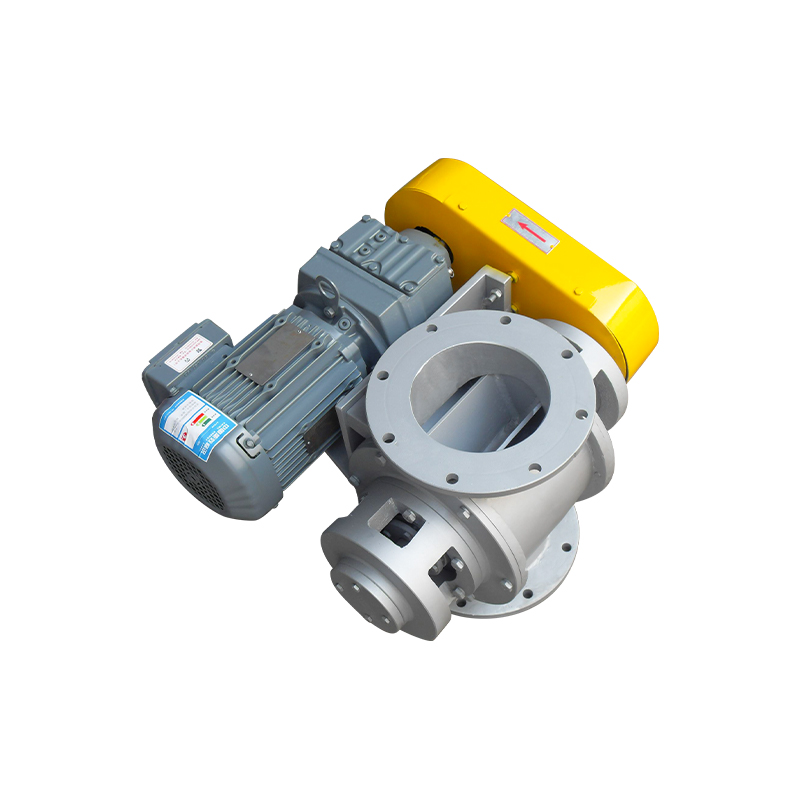
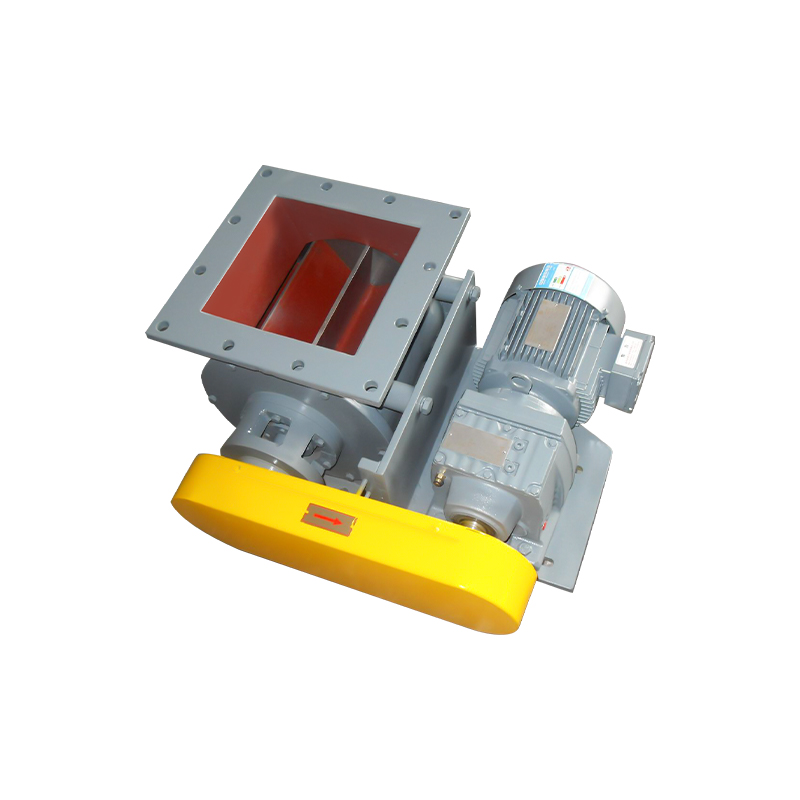
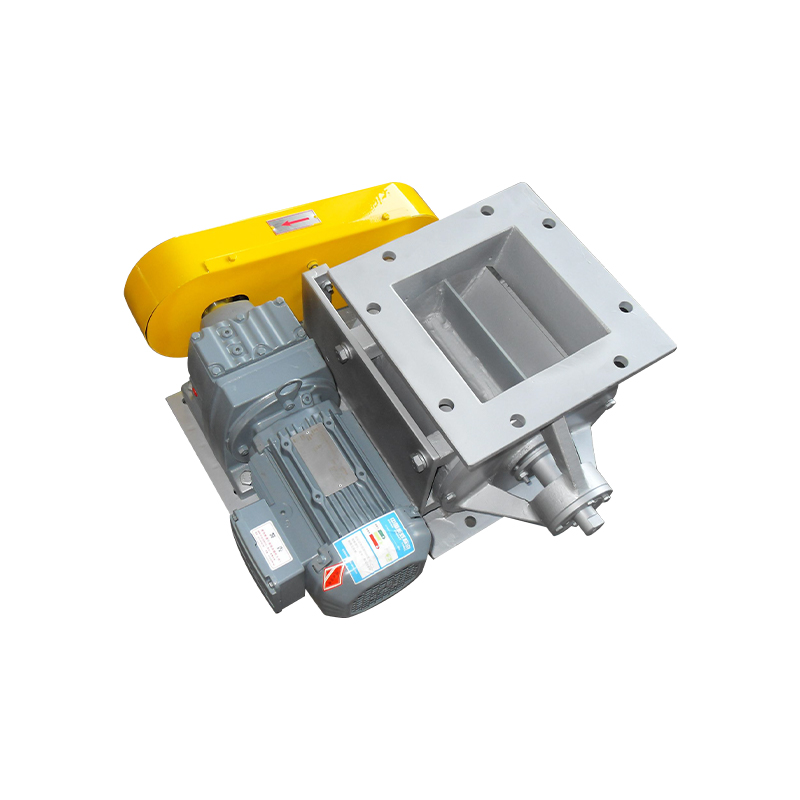
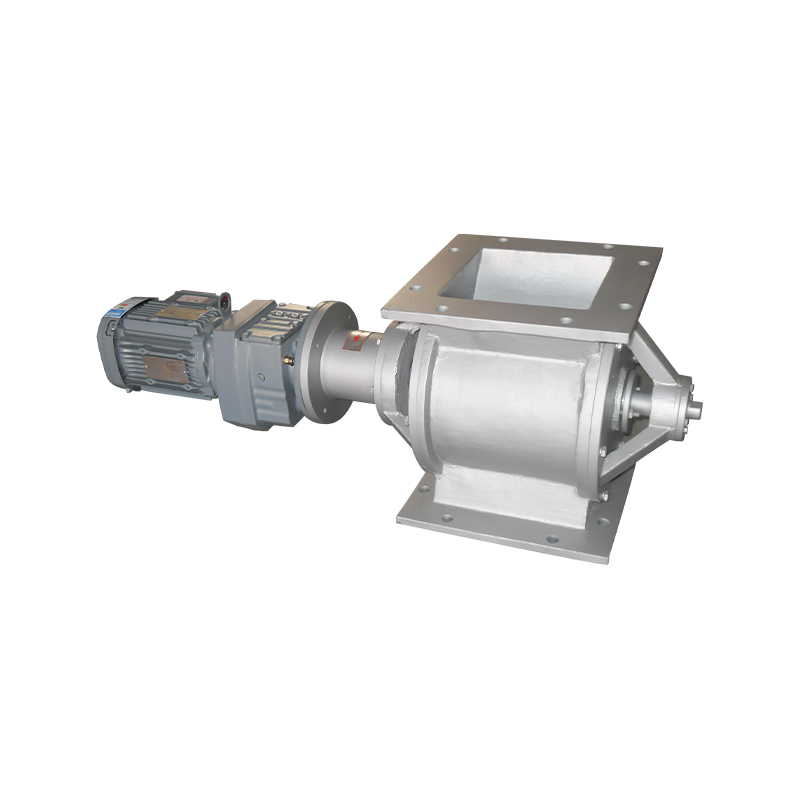
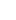
A purging or air swept round port rotary valve is a specialized component widely used in pneumatic conveying and bulk material handling systems. Its primary function is to control material flow while maintaining pressure differentials between upstream and downstream processes. By introducing purge air around the rotor tips and shaft seals, these valves significantly reduce material buildup, air leakage, and component wear, making them ideal for demanding and continuous operations.
Selecting a high-efficiency air swept round port rotary valve requires a thorough understanding of process conditions, material characteristics, sealing performance, and system integration. The following sections explore the most critical factors to consider during selection.
Material Characteristics and Handling Requirements
The physical properties of the conveyed material play a decisive role in rotary valve selection. Air swept designs are particularly beneficial for powders and granules that are abrasive, sticky, hygroscopic, or prone to compaction. Particle size distribution, bulk density, flowability, and moisture content all affect how material interacts with the valve rotor and housing.
Fine powders, such as cement, flour, or chemical additives, often require enhanced air purging to prevent packing at the rotor tips. Coarser or irregular particles demand sufficient pocket volume and clearance to avoid jamming and excessive torque loads.
Operating Pressure and System Configuration
Air swept round port rotary valves are commonly installed in pneumatic conveying systems operating under positive or negative pressure. Understanding system pressure differentials is essential to ensure proper sealing and efficiency. High pressure systems require robust housings, precision-machined components, and effective purge air distribution to minimize leakage.
Valve orientation, whether feeding into a conveying line or discharging from a cyclone or filter receiver, also influences performance. Proper alignment with round pipelines reduces turbulence, improves flow consistency, and minimizes energy losses.
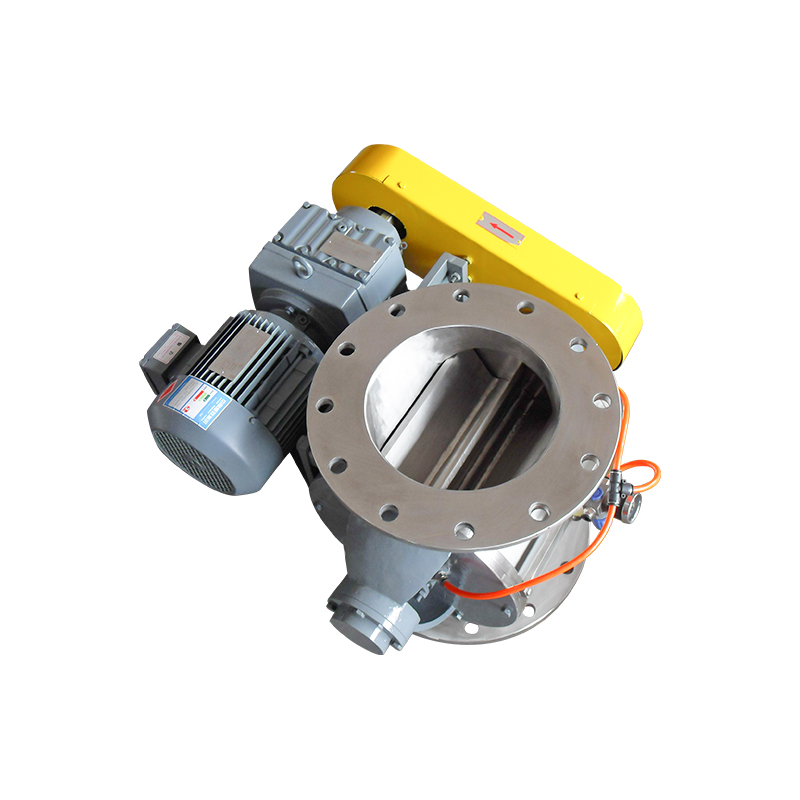

Air Purge and Swept Design Efficiency
The defining feature of an air swept rotary valve is its integrated purge air system. Purge air is introduced through dedicated channels to create a protective air barrier between the rotor tips and housing. This design prevents fine particles from entering critical clearances, reducing wear and maintaining consistent performance over time.
Purge Air Pressure and Flow Control
Selecting the correct purge air pressure and flow rate is vital. Insufficient purge air may allow material ingress, while excessive air can disrupt conveying balance and increase energy consumption. High-efficiency valves are designed to achieve optimal sealing with minimal purge air usage, improving overall system efficiency.
Rotor Design and Pocket Geometry
Rotor configuration directly affects throughput, feeding consistency, and air leakage. Round port rotary valves typically feature rotors optimized for smooth material entry and discharge into circular pipelines. Pocket depth, number of vanes, and rotor diameter should be matched to the desired capacity and material flow rate.
For fragile or degradable materials, gentle pocket geometry minimizes breakage. For abrasive materials, hardened or coated rotors improve wear resistance and extend service life.
Housing and Construction Materials
Valve housing materials must be compatible with both the conveyed product and the operating environment. Cast iron housings are common for general industrial use, while stainless steel is preferred for food, pharmaceutical, and corrosive applications. High-efficiency air swept valves often use precision-machined housings to maintain tight tolerances and consistent purge air distribution.
Surface finishes and optional wear liners can further enhance durability, particularly in high-throughput or abrasive service conditions.
Sealing Systems and Leakage Control
Effective sealing is one of the main reasons for choosing an air swept rotary valve. Shaft seals, end covers, and rotor tip clearances must work together to minimize air leakage while allowing smooth rotation. Advanced sealing designs, combined with purge air, significantly reduce product contamination and maintain pressure integrity.
When selecting a valve, consider the type of shaft seals used, their service life, and ease of replacement. Reduced leakage directly translates to improved conveying efficiency and lower operating costs.
Drive System and Power Requirements
The drive system must be capable of handling the torque required to rotate the valve under load. Factors such as material bulk density, pressure differential, and rotor speed influence motor sizing and gearbox selection. High-efficiency rotary valves are designed to operate smoothly with stable torque characteristics, reducing energy consumption and mechanical stress.
Variable speed drives are often recommended to allow fine adjustment of feed rates and optimize system performance under changing process conditions.
Maintenance, Reliability, and Service Life
Ease of maintenance is a key consideration in valve selection. Air swept round port rotary valves with modular designs allow faster inspection, cleaning, and replacement of wear parts. Reduced material buildup and lower wear rates contribute to longer service intervals and improved reliability.
Selecting a valve with proven durability and readily available spare parts minimizes downtime and supports long-term operational stability.
Compliance and Application-Specific Requirements
Depending on the industry, additional requirements may apply. Food and pharmaceutical applications often require FDA-compliant materials and hygienic designs. Chemical and hazardous material handling may demand explosion-proof motors, pressure-rated housings, or special coatings. Ensuring compliance with relevant standards is essential when selecting a high-efficiency air swept rotary valve.
Key Selection Factors Comparison
| Factor | Recommended Focus | Benefit |
| Material Properties | Flowability, abrasiveness | Prevents blockage and wear |
| Purge Air Design | Controlled pressure and flow | Reduces leakage and buildup |
| Rotor Geometry | Optimized pocket design | Stable feeding and efficiency |
| Sealing System | Advanced shaft and tip seals | Maintains pressure integrity |
Conclusion
Selecting a high-efficiency purging or air swept round port rotary valve involves more than matching size and capacity. Careful evaluation of material behavior, purge air design, rotor configuration, sealing performance, and system conditions ensures reliable operation and long-term efficiency. By focusing on these critical factors, operators can achieve consistent material flow, reduced maintenance, and optimized pneumatic conveying performance.


 English
English عربى
عربى